ABOUT CANCER
disease and how you can best support them during their treatment.
Breast cancer happens when cells in the breast grow out of control. These cells are
called tumours and can only be seen using x-ray or noticing a lump.
A tumour is malignant (cancer) if it surrounded by tissue or spread (Metastasized) to
distant areas of the body. This is what happens in someone with breast cancer which
strike both men and women.
The taboo about cancer
If you are feeling down talk with someone you trust about your disease it will helps you deal with your new worries. Talking about your feelings openly and honestly with someone you trust, a psychologist or counsellor will help to cope with the ever-changing emotions you may feel on your cancer journey.
Many people associate the cause of having cancer with something they have done wrong. The truth is cancer can happen to anyone.
Because of genes inherited at birth some people are more likely to develop a cancer but you are not to blame.
When it comes to cancer there are so many factors to take into consideration. Yes, our unhealthy habits can increase the risk of developing errors in our cells but with most cancers, doctors rarely know the exact cause, so chance plays a huge part in having a cancer.
Most cancers are not due to an inherited gene but start because of an error in copying DNA. This happens when cells are in the process of dividing and growing. These errors happen before a cell becomes cancerous.
What is a Tumor?
A tumor is malignant (cancer) also knows as neoplasm is an irregular mass of tissue. This can be solid or in a fluid-filled form. It is important to note that not all tumors are cancerous.
Where do my cancer cells came from?
Our cells in our bodies all have certain jobs to do. We all have Normal cells. These cells can divide, grows and die when they are worn out or damaged. Some of these dead cells becomes active and grow because of mutation or genetic conditions in the body to form cancer cells. They can also become active due to environment condition or lifestyle like drinking or smoking heavily.
Are cancers different?
Every cancer is different. Some are more active and grows faster than the others. They also response to treatment differently. Some types of cancer are treated with surgery; others respond better to drugs called chemotherapy. In most cases two or more treatments are used to get the best results.
I am told I have Cancer
They just told me I have cancer. This is hard. What should I do?
Yes, it is hard indeed and there is a fear that goes through your mind when you’re told you have cancer. But you must do the right thing which is get proper diagnosis to know the extent of your cancer. There is risk involved therefore, timely or early diagnosis and treatment is essential. It’s hard to think about your diagnosis every but this is not a death sentence and your cancer can be treated.
What Is Cancer?
Cancer can start in any part of the body and is not limited to the old and young even babies can be born with the disease. Our bodies are made up of hundred million and millions of cells when these cells grow out of control and crowd out normal cells they form cancer. Some cancers start from blood cells they are called leukaemia. They don’t form solid tumors instead, the cells are build up in the blood and sometimes bone marrow. Cancer makes it hard for the body to work the way it should.
Is Cancer Curable?
Yes, it is but it also depends at the stage at which it is. Many people are now living lead full lives after cancer treatment than before. A lot of advances in cancer medical research has led to a better treatment and diagnoses of the diseases. The early cancer is detected the better the chances of survival. Cancer are treated with surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation Surgery to take out the cancer.
Cancer basics
Cancer can start in any part of the body. It can be in the lungs, the breast, the colon, or even in the blood. Cancers are similar in many ways but also different. It is just not one disease there are many types of cancer. When they grow unchecked they can and spread very rapidly.
What stage is the cancer?
A cancer stage is normally the spread of the disease from where it started. Often people talk of cancer stage 1 or 2. This means the cancer is at a lower stage and has not spread too much. Tests are normally done to determine the stages of the cancer. Knowing the stage of the cancer helps the doctor decide what type of treatment is best. The higher the stages such as a stage 3 or 4 means it has spread more. Stage 4 is the highest stage. Doctors are normally good at explaining the stage of your cancer and what it means for you.
TYPES OF CANCER
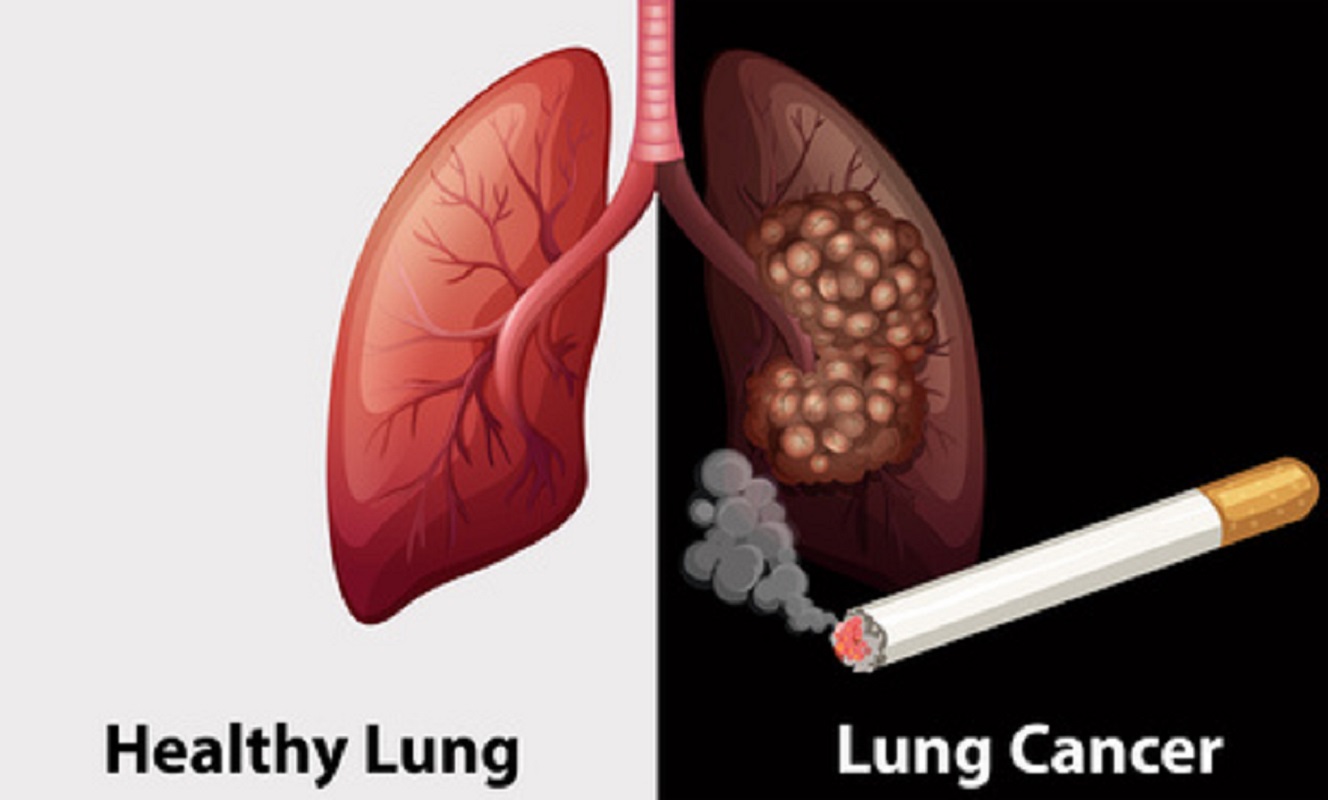
Lung Cancer
In some parts of world there are no medical facilities to diagnoses people with lung cancer often think they have Tuberculosis(TB) because the symptoms are very much similar. TB can increase the risk of developing lung cancer therefore; it is important to get proper diagnoses. Prevention of lung cancer is possible through cessation of smoking or inhaling fumes in an enclosed kitchen such as those in Sierra Leone The symptoms of lung cancer are persistent coughing Coughing of blood Shortness of breath Weight loss and tiredness some level discomfort or pain around the chest area when coughing. collection of fluid in the pleural cavity which is the cause of the breathlessness In some cases, there are no symptoms at all. Therefore, a test to diagnose secondary cancer in the lung through X-ray of the chest, Biopsy, PET or CT may be required.
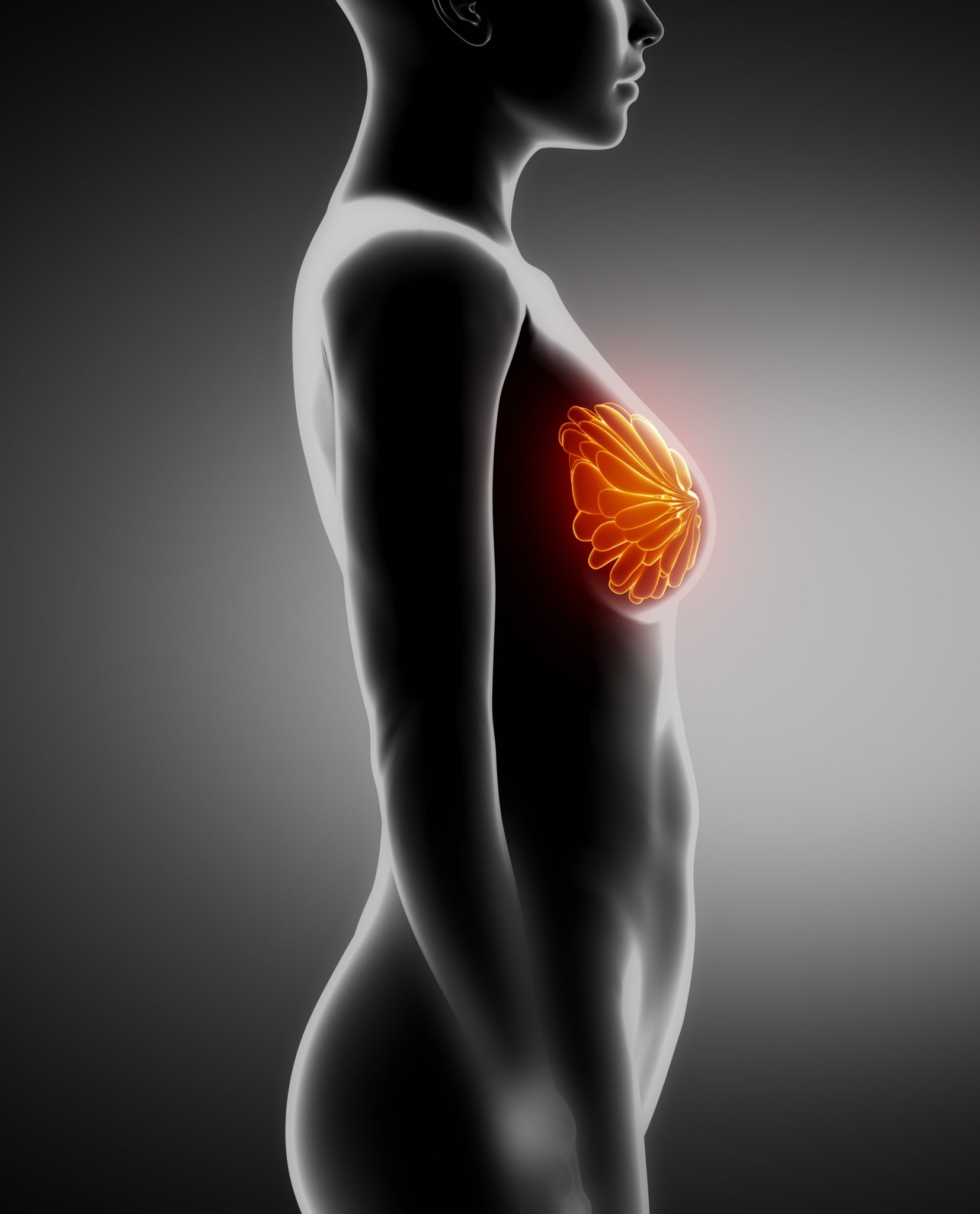
Breast Cancer
The most common symptom of breast cancer is a lump in the breast area but there are other symptoms to watch for. The risk of developing breast cancer may increase with age and lifestyle such are alcohol intake, smoking and being overweight There are several types of breast cancer. These are as follows:
invasive lobular breast cancer
Paget’s disease of the breast ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) triple negative breast cancer lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) invasive ductal breast cancer breast cancer in men. HER2 positive breast cancer inflammatory breast cancer You can read about these one the internet.
Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid cancer can cause any of the following signs A lump in the neck that feels firm and does not easily move around under the skin, sometimes growing quickly Swelling in the neck the makes it swallow Pain in the front part of the neck, sometimes the pain is up to the ears Hoarseness or other voice changes that do not go away Trouble breathing Persistent coughing that is not due to a cold
In some cases thyroid cancer hormones may cause diarrhoea and sometimes flushing.
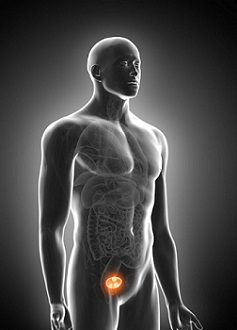
Prostate Cancer
It is more common in the elderly but young men are also susceptible to the disease.They can include any of the following: Difficulty passing urine passing urine more frequently than usual especially at night the feeling of not completely emptying your bladder needing to rush to the toilet to pass urine Other extremely symptoms are blood in the urine or semen and pain when urinating or ejaculating In some cases, the first symptom of prostate cancer may be pain in the spine, hips, pelvis or legs. This is because prostate cancer can sometimes spread to the bones.

Bowel/Colon Cancer
The symptoms of bowel cancer may include:
blood in, or on, your stools (bowel motions) – the blood may be bright red or dark a change in your normal bowel habit, such as diarrhoea or constipation, that happens for no obvious reason and lasts longer than three weeks unexplained weight loss pain in the tummy (abdomen) or back passage feeling that you haven’t emptied your bowel properly after a bowel motion unexplained tiredness.
Leukaemia
The symptoms of leukaemia include: excessive sweating night Tiredness and weakness that often don’t go away even with rest
Weight loss Pain in the bone and tenderness Swollen painless lymph specially in the neck and armpits Liver or spleen enlargement
Petechiae which are red spots on the skin Bruising and bleeding easily Fever or chills Frequent infections
Ovarian Cancer
Loss of appetite and quick to feeling full Stomach or pelvic pain.Feeling to pass urine urgently or more frequently than normal.
changes in bowel habit and feeling bloated Feeling tired.Weight loss.


Cervical Cancer
When abnormal cells do develop into cervical cancer, some of the symptoms you may have include:
Irregular vaginal bleeding smelly vaginal discharge.pain during or after sex.vaginal bleeding after the menopause.blood-stained vaginal discharge.pain in your pelvis or lower back.
Skin Cancer
The first sign of non-melanoma skin cancer is usually the appearance of a lump or discoloured patch on the skin that continues to persist after a few weeks, and slowly progresses over months or sometimes years. This is the cancer, or tumour.
In most cases, cancerous lumps are red and firm and sometimes turn into ulcers, while cancerous patches are usually flat and scaly.
Non-melanoma skin cancer most often develops on areas of skin regularly exposed to the sun, such as the face, ears, hands, shoulders, upper chest and back.

